New Paradigms in Banking IT 7/2012
Summary
Deutsche Bank is an early adopter of new technologies. On July, 2nd 2012 the bank launched a new, first of its kind high performance IT platform, named “Magellan”. Magellan replaces Deutsche Bank’s more than 40 years old legacy core banking system and is based on SAP Banking Services and GRID computing in the core. It enables the bank to reduce its IT and operations costs by 200 million Euro in 2012. Total estimated program costs are about Euro 1 billion until 2015. Four general paradigm-shifting Banking IT principles can be identified behind Deutsche Bank’s Magellan platform:
-
1.User interfaces: From functional to productivity oriented
-
2.Processes: From fix coded to flexible
-
3.Service: From application centric to service oriented and packaged
-
4.Infrastructure: From high variety to industrialized and low cost
Over the next couple of years I expect the majority of banks to follow Deutsche Bank’s route, globally.
Deutsche Bank is an early adopter of new technologies
Deutsche Bank has been an early adopter of new technologies for decades. In 1983 the bank started one of the first German electronic banking services. 12 years later, in 1995, Deutsche Bank launched one of the first German Internet Banking services. In 2000 the bank launched the first secure Mobile Banking service, globally and in 2007 Deutsche Bank introduced the first service-oriented architecture with significant re-use of business functions in banking.
Magellan: A first of its kind high performance IT platform
On July, 2nd 2012 Deutsche Bank launched a new, first of its kind high performance IT platform, named “Magellan”. Magellan replaces Deutsche Bank’s more than 40 years old legacy core banking system and is based on SAP Banking Services and GRID computing in the core. It enables Deutsche Bank to reduce its IT and operations costs by 200 million Euro in 2012.
The new IT platform also builds the basis for the technological integration of Deutsche Bank’s latest acquisition: Postbank. In future the platform will handle about 24 million retail banking customers.
Magellan was planned between 2005 and 2009. The program started in January 2010. Total estimated program costs are about 1 billion Euro until 2015.
At this point in time this program is the largest core banking system transformation, globally and Deutsche Bank shifts traditional paradigms in Banking IT.
New paradigms in Banking IT
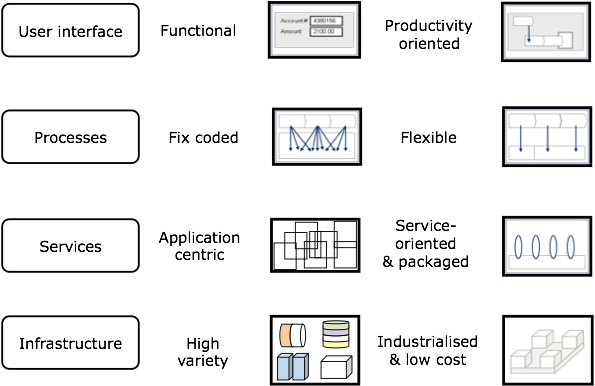
Four general paradigm-shifting Banking IT principles can be identified behind Deutsche Bank’s Magellan platform:
1. User interface: From functional to productivity oriented user
Regarding the user interface of IT systems banks traditionally focussed to push new IT functionality as fast as possible to the users – bank staff and bank customers. Usability and user productivity enjoyed a low priority. Today most banks have implemented thousands, sometimes ten thousands of banking functions. The new challenges now are usability and productivity: How do IT systems support and increase the productivity of bank staff and the usability for bank customers?
2. Processes: From fix coded to flexible
Still almost 75% of banks run self developed IT systems based on COBOL, globally. The programming language COBOL was created in 1959. Given their age most COBOL programs in banks are fix-coded. That led to difficult and expensive to change processes. The speed of business change, consolidation and regulatory regulatory requirements in the banking industry require modern Banking IT platforms that are cost efficient and flexible to change. Only Banking IT platforms based on modern object-oriented programming languages like C++ or Java comply with these requirements.
3. Services: From application centric to service oriented and packaged
Traditionally all banks are early adopters of information technology. Over the last five decades banks have spend several hundred billions Euro on IT and have employed hundred thousands of IT specialist to develop own custom made financial applications.
In the last decade we have seen the rise of standard software for financial institutions and the introduction of flexible service oriented software architectures in banking. In general IT products and applications for banks and IT service providers matured. And banks started to buy more and more software packages instead of in-house development.
Going forward, the higher the maturity of IT products and services offered by IT providers, the more banks will introduce and integrate service oriented and packaged IT products into their IT landscapes.
4. Infrastructure: From high variety to industrialized and low cost
In most banks we can identify several technologies and infrastructures of the last five decades, like COBOL and mainframe, C/C++ and midrange, client-server and latest web technologies. Most of these technologies are legacy. As a consequence, the current IT landscapes of banks have too many interfaces, file transfers and point-to-point connections. There are not intended dependencies between business logic and technology, not intended dependencies exist within the various layers of technology and there is a overlapping of applications across functionalities. In summary this leads to significantly high IT operations and maintenance costs. In many cases banks spend more than 80% of their available IT budget to run the bank.
But the IT industry matured over the last two decades. Today there are standard software for banks, established technology standards, mature technologies that enable banks to introduce cheap, industrialized standard hardware and infrastructure.
In that context I am aware of projects and programs and I have some own experiences that led to costs reductions up to 80%.
Outlook
Over the next couple of years I expect the majority of banks to follow Deutsche Bank’s route, globally.
Links
https://www.deutsche-bank.de/medien/en/content/3862_4172.htm, Deutsche Bank launches high performance retail banking platform

“Those who remain on the coast,
can not discover new oceans.”
Ferdinand Magellan
How Deutsche Bank transforms its legacy IT Landscape
based on SAP Banking and GRID computing in the core